
The hidden file is still listed, but the “.” and “.” entries are suppressed. If you don’t want your listing cluttered up with the “.” and “.” entries, but you do want to see hidden files, use the -A (almost all) option: ls -l -A A file called “.base_settings” is now visible for the first time. For example, the following respectively print the first and last 10 lines of the huge logfile ‘ /var/log/syslog ‘. Similar tail prints the last 10 lines of a file. The head command is used to print the first 10 lines of a file, instead of printing the whole file. The closest you can get is the files ctime, which is not the creation time, it is the time that the files. In practice, most filesystems do not record that information and the linux kernel does not provide any way of accessing it. The two entries “.” and “.” represent the current directory and the parent directory, respectively. View File Contents Using head or tail Commands. In theory, with GNU stat you could use stat -c w or W to get a files creation date (aka birthtime).

To see hidden files, use the -a (all) option: ls -l -a To see the file sizes in the most appropriate units (Kilobytes, Megabytes, etc.) use the -h (human-readable) option: ls -l -h Having the file sizes in bytes is not always convenient. They are followed by the file size and the date of the last modification of the file. The name of the owner and group are displayed next. If this is set, regardless of the write and executable privileges that are set on the files in the directory, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root user can rename or delete files in the directory. The execution permission for the others can sometimes be represented by a t. lsusb- List usb buses and device details. When used with a directory, any files created inside it will take their group permissions from the directory they’re being created in, not from the user who is creating the file. Basic Linux Commands to Check Hardware and System Information Printing Machine Hardware Name (uname m uname a) lscpu. When this is applied to a file, it means the file will be executed with the privileges of the ower’s group. The execution permission for the group can also be an s. If you want to save a list of the files in your directory to a file named foo, you would use the following command. As with many other Unix commands, you can redirect the output from ls to a file, or pipe it to another command.
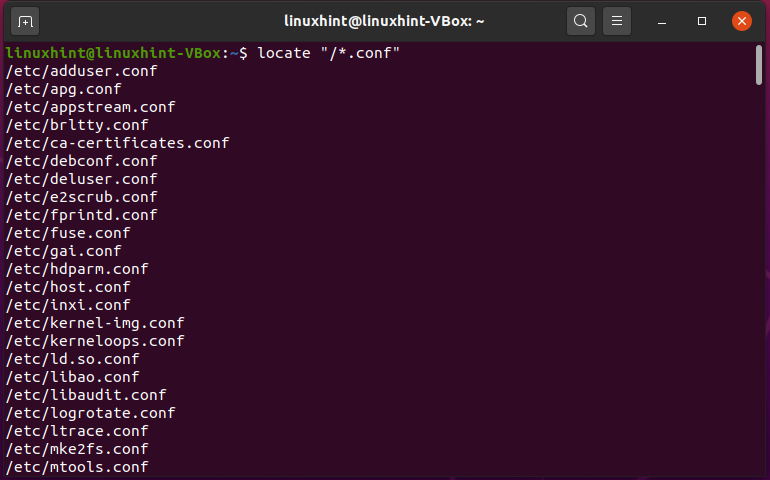
If it is present, it means that the file is executed with the privileges of the file owner, not the user executing the file. To list all the files in a directory in the long format, with marks for the types of files, you would enter: ls -Flg. With the help of this command, we can find the properties of file such as file size. Sometimes the execution permission for the owner is represented by an s. This command is used to display the information of files and filesystem. The second set of three permissions are for group members, and the last set of three permissions is for others. The first set of three characters are the permissions for the file owner.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
